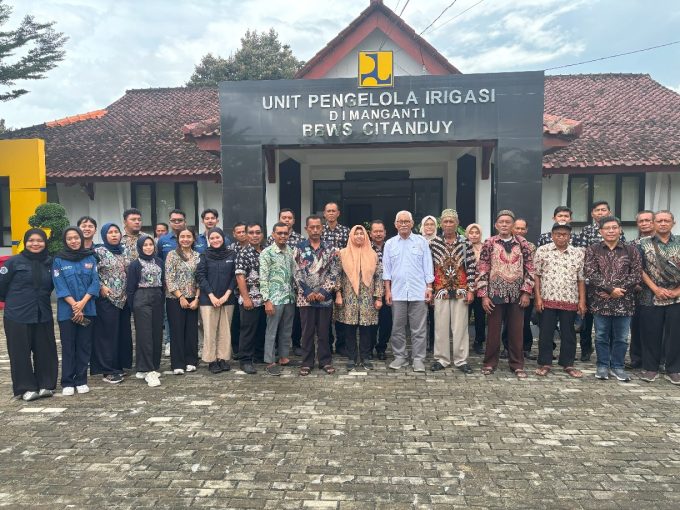
Ciamis, May 6–7, 2025 — A group of academics from the Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (DTPB), Faculty of Agricultural Technology (FTP), Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), consisting of lecturers, research assistants, and students, served as facilitators in a socialization and Focus Group Discussion (FGD) event aimed at evaluating the modernization of irrigation in the Manganti Irrigation Area (D.I. Manganti). This irrigation area, which serves as a pilot project for the digitalization of irrigation systems, spans 26,153 hectares and covers two provinces and three districts: Ciamis and Pangandaran in West Java, and Cilacap in Central Java. The evaluation activity is part of the Strategic Irrigation Modernization and Urgent Rehabilitation Project (SIMURP) and was held in collaboration with the Directorate of Technical Guidance for Water Resources, Directorate General of Water Resources, Ministry of Public Works, and the Citanduy River Basin Organization (BBWS Citanduy) as the implementing unit.
Held at the Office of the Irrigation Management Unit (UPI) of D.I. Manganti, the event was attended by representatives from the Directorate of Technical Guidance for Water Resources, BBWS Brantas, DTPB FTP UGM academics, and stakeholders in irrigation management, including provincial/district Public Works Services, provincial/district Agricultural Services, Regional Development Planning Agencies (Bappeda), UPI, and farmer representatives from Water User Associations (P3A). The event was opened with a speech from the Director of Technical Guidance, Directorate General of Water Resources, Dr. Ir. Muhammad Rizal, M.Sc., represented by Dr. Dian Kamila, S.T., M.T., Head of the Data and Water Resources System Development Sub-directorate. This was followed by a speech from the Head of BBWS Citanduy, Dr. Ir. Elroy Koyari, S.T., M.T., and a presentation on the D.I. Manganti irrigation system and its digitalization by the Head of Operation and Maintenance Division, BBWS Citanduy, Mohammad Ramdani, S.T., M.Sc.
The socialization program was divided into two sessions: presentations on irrigation modernization policy evaluations and interviews with various stakeholders. The first presentation was delivered by Prof. Dr. Ir. Sigit Supadmo Arif, M.Eng., a lecturer from DTPB FTP UGM, and Dr. Asna Mustofa, S.T.P., M.P., from the Faculty of Agriculture, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman (Unsoed), who explained the concepts and implementation stages of irrigation modernization. The second presentation was delivered by Dr. Eng. Ansita Gupitakingkin Pradipta, S.T., M.Eng., also a lecturer from DTPB FTP UGM, who highlighted the urgency of evaluating irrigation modernization and its implementation methods, with a link to environmental issues such as climate change. The second session of the socialization involved interviews with stakeholders to gather inputs for the evaluation.
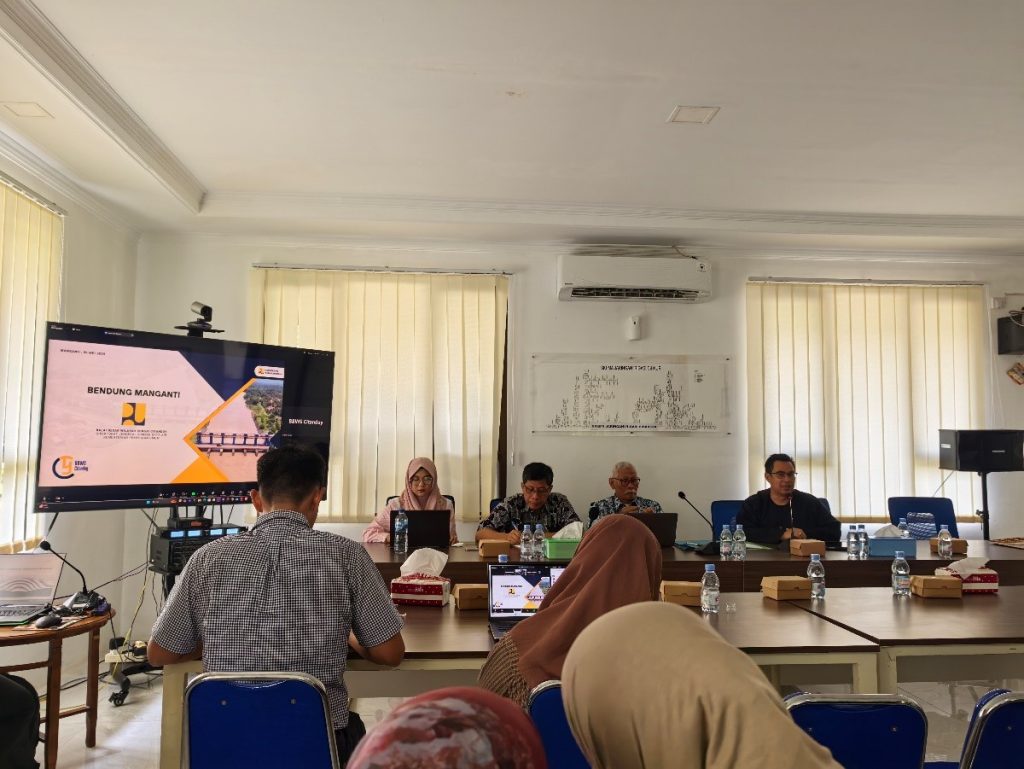

The second day featured a Focus Group Discussion (FGD) aimed at mapping field conditions, identifying problems, gathering stakeholder aspirations, and formulating future solutions. The FGD was facilitated by research assistants from the UGM FTP Center for Irrigation and Agricultural Modernization Studies (PKMIP): Arya Jaya Kusuma, S.T.P., Nindya Marsya Larasati, S.Sos., and Tsabita Prameswari Jannati, S.I.P. The team opened the discussion with a presentation on community participation in irrigation modernization. Hot topics in the FGD included water availability and its distribution to farmland, implementation and challenges in the operation and maintenance (O&M) of irrigation networks, institutional roles in irrigation management, and environmental factors impacting irrigation O&M. Key environmental issues discussed included heavy sedimentation in the Citanduy River Basin and saltwater intrusion into paddy fields. The irrigation modernization evaluation team also conducted field inspections to verify actual conditions on-site.
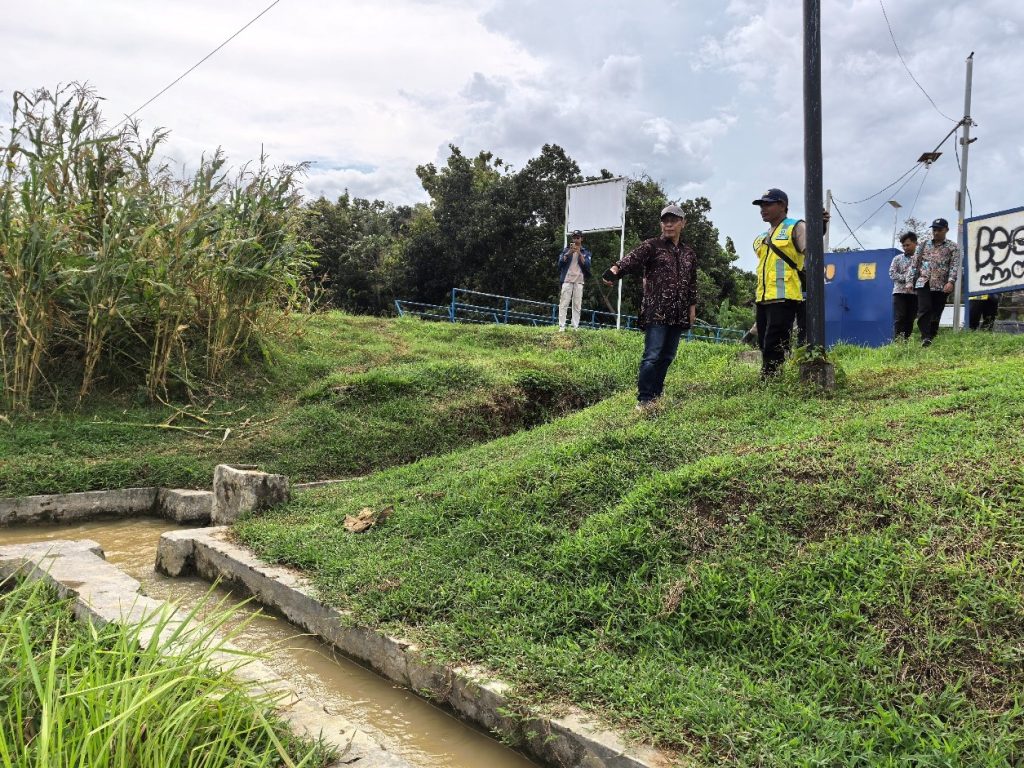

The data and insights gathered from this socialization and FGD event will serve as valuable input for evaluating the implementation of irrigation modernization in D.I. Manganti and shaping future policy directions. This activity is part of broader efforts to support the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 2: Zero Hunger, by enhancing agricultural productivity through adaptive and sustainable irrigation systems.