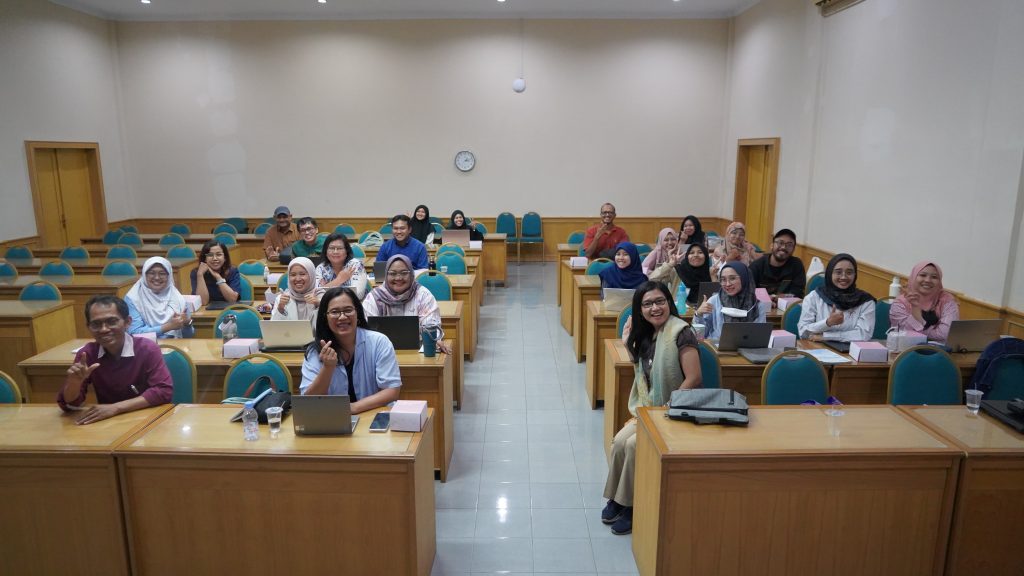
Yogyakarta, 30 September 2025 – The Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (DTPB), Faculty of Agricultural Technology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (FTP UGM), through its Master’s and Doctoral Programs, organized a Bibliometric Miniclass Training. The session featured Mr. Janu Saptari, S.IP., senior librarian from UGM Library and Archives, as the speaker. The training was attended by DTPB FTP UGM postgraduate students, aimed at preparing them for academic article writing and introducing UGM Library facilities, both online and offline, to support academic writing activities.
The training was divided into two sessions. The first session was a lecture delivered by Mr. Janu, covering key stages in bibliometric analysis: from collecting publication data via scientific databases such as Scopus, ensuring data validity and consistency through data cleaning, conducting quantitative analysis of publication counts, authors, keywords, and citations, to visualizing data using software such as VOSviewer to illustrate citation networks and author collaborations. In the final stage, participants were guided to interpret the results to identify patterns, clusters, and insights relevant to research.
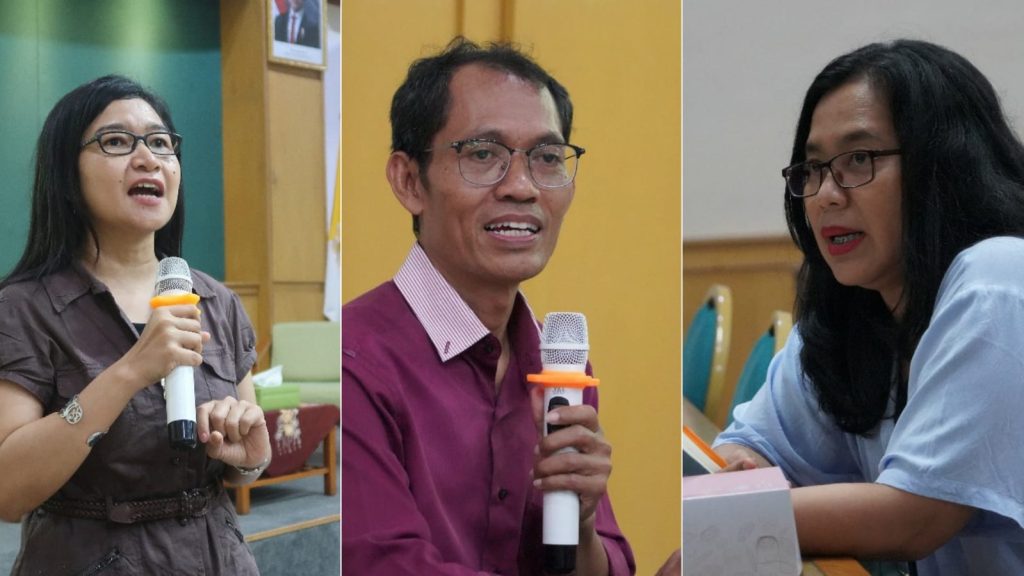

The second session focused on hands-on practice. Students applied the materials presented to conduct their own bibliometric analyses. Through this approach, participants not only gained theoretical understanding but also developed technical skills that can be applied to their research.
This activity aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly Goal 4 (Quality Education) and Goal 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure). By equipping students with bibliometric skills, DTPB FTP UGM contributes to improving the quality of scientific publications, fostering research innovation, and strengthening academic competitiveness at both the national and international levels.

Through this training, postgraduate students of DTPB FTP UGM are expected to be better prepared to produce high-quality scientific works, contribute to the advancement of knowledge, and respond to global research challenges that demand collaboration and openness of information.