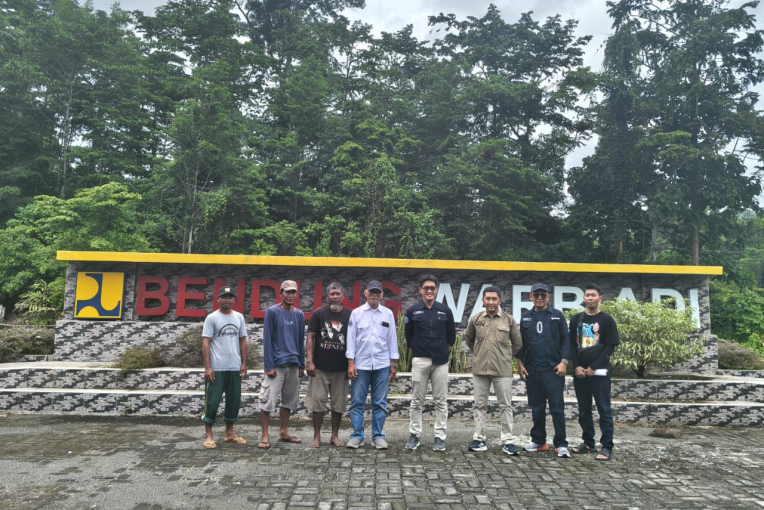
MANOKWARI, WEST PAPUA – A research team from the Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, Faculty of Agricultural Technology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) has completed a series of surveys and coordination activities in Manokwari, West Papua, on November 11–14, 2025. This visit was part of the implementation initiative of the Discharge Monitoring System (SIPASI) for irrigation modernization in Oransbari Irrigation Area, aiming to support food security and sustainable water resource management.
The UGM team, bringing expertise in agricultural and biosystems engineering, consisted of Prof. Sigit Supadmo Arif, Dr. Andri Prima Nugroho, Rohmad Basuki, STP., and Yeste Sujut Triyanta. The team traveled from Yogyakarta on Tuesday afternoon, November 11, heading to Manokwari via Makassar.
Meeting with West Papua River Basin Organization (BWS Papua Barat)
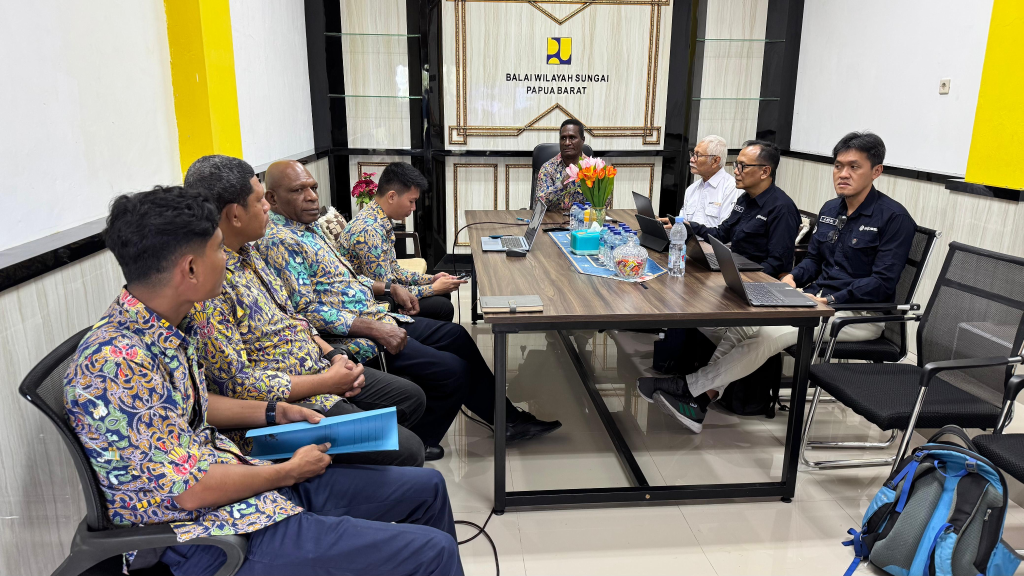

On Wednesday, November 12, the first agenda was a meeting with the Head of West Papua River Basin Organization (BWS Papua Barat), Mr. Wempy Nauw, along with technical representatives. The meeting served as an important step to align perspectives on the SIPASI implementation plan in Oransbari Irrigation Area.
During the discussion, BWS Papua Barat presented current irrigation conditions, field challenges, and expectations related to improving discharge data accuracy using modern monitoring systems. The UGM team introduced the SIPASI concept, including sensor and telemetry integration, real-time data acquisition, and Knowledge Management System development. The Head of BWS expressed full support for this modernization program and emphasized the importance of collaboration between technical institutions, field operators, and irrigation officers.

Field Survey in Oransbari Irrigation Area
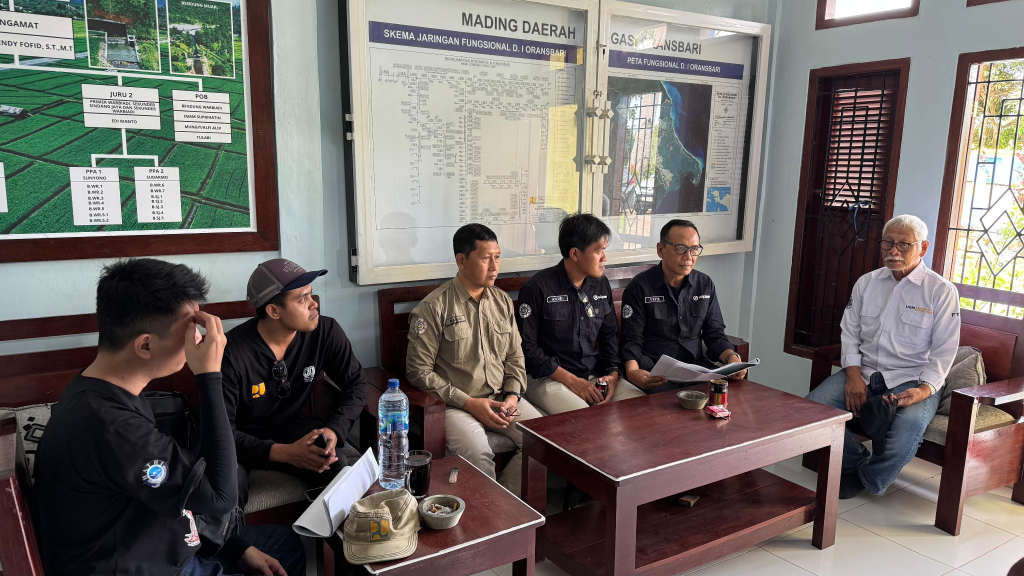

On Thursday, November 13, the activities continued with a comprehensive field survey in Oransbari Irrigation Area, South Manokwari. Supported by expertise in sustainable agricultural technology, the team conducted field observations from the upstream structure to the farming area to gather technical details.
The survey included Oransbari Suplesi Weir, focusing on its structure, discharge control mechanisms, and potential installation points for discharge sensors, gate-opening sensors, and automatic actuators. The team also traced the irrigation network—primary and secondary canals, division structures, and intake points—identifying strategic locations for monitoring and automation with irrigation operators.
Infrastructure Assessment and Local Agricultural Practices
In addition to the hydraulic survey, the team assessed supporting aspects of modernization, such as cellular network coverage for telemetry, solar panel power potential, device security, and site accessibility. The field visit continued to Warbiadi rice fields, where the team observed local irrigation practices, cropping patterns, and the use of modern agricultural machinery.
The results of this field survey provide a strong foundation for designing a precise and efficient irrigation modernization plan tailored to the local West Papua context.
Contribution to SDGs and Sustainable Agriculture
This initiative directly supports the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including:
-
SDG 2 – Zero Hunger through increased agricultural productivity
-
SDG 6 – Clean Water and Sanitation via efficient water management
-
SDG 9 – Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure through modern irrigation technology development
The collaboration is expected to enhance irrigation performance, strengthen food security, and accelerate sustainable agricultural development in West Papua.